Introduction
\n
As we move closer to 2025, the landscape of digital currencies is evolving at an unprecedented pace. A staggering $4.1 billion was lost to hacks in decentralized finance (DeFi) in 2024, spotlighting the need for robust security measures in the cryptocurrency sphere. The rise of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) is a major focal point, particularly as they stand in contrast to private cryptocurrencies. This article unpacks the significance of CBDC vs private cryptocurrency in 2025, while addressing market trends and potential implications for nations such as Vietnam, where digital asset adoption is rapidly increasing.
\n\n
Understanding CBDCs and Private Cryptocurrencies
\n
Before delving into the nuances of CBDCs and private cryptocurrencies, it’s essential to define both terms.
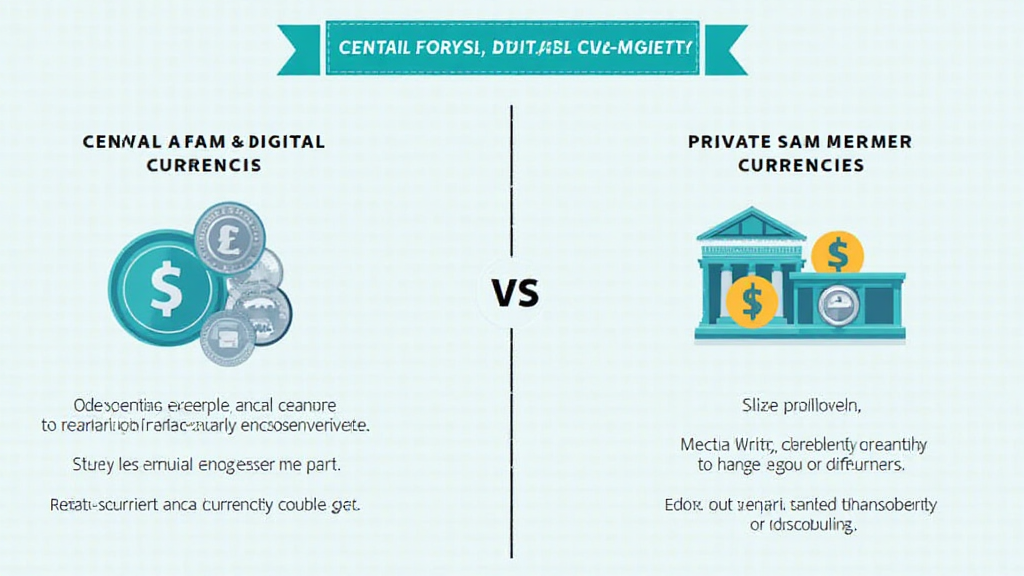
CBDCs are digital forms of a country’s fiat currency issued by the central bank, while private cryptocurrencies are decentralized currencies developed by individuals or companies, like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
\n
Key Differences:
 \n
\n
- \n
- Control: CBDCs are regulated by a central authority, which grants them stability and regulatory oversight. In contrast, private cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized platforms without central governance.
- Privacy: CBDCs may allow for transaction tracking, whereas private cryptocurrencies prioritize user anonymity.
- Use Cases: CBDCs are intended to enhance payment efficiency and financial inclusion, while private cryptocurrencies often serve as an alternative investment or store of value.
\n
\n
\n
\n\n
The Rise of CBDCs: A Global Perspective
\n
As of 2025, more than 80% of central banks worldwide are exploring or are in the process of implementing CBDCs. Countries like China with its digital yuan and Sweden with its e-krona are leading the charge. Vietnam is not far behind, with increased discussions around the tiêu chuẩn an ninh blockchain to safeguard the digital economy.
\n\n
Impacts of CBDCs on Traditional Banking
\n
The introduction of CBDCs poses significant implications for traditional banks. Here’s a breakdown of how CBDCs might reshape banking:
\n
- \n
- They could offer lower transaction costs and faster transfer times.
- Transition towards a cashless society becomes more feasible.
- Direct access to central bank reserves may blur the lines between consumer banking and central banking.
\n
\n
\n
\n\n
Private Cryptocurrencies: The Contrarian Spirit
\n
Despite the government-backed CBDCs, private cryptocurrencies are gaining traction among users who value decentralization and privacy. In Vietnam, the growing interest in private cryptocurrencies is reflected by a 15% growth in users from the previous year.
\n\n
The Appeal of Decentralization
\n
Users gravitate towards private cryptocurrencies for various reasons:
\n
- \n
- Autonomy: Users can manage their assets without relying on a centralized authority.
- Potential for High Returns: As the 2025 trend shows, altcoins like Polkadot are regarded as some of the most promising investments.
- Diverse Use Cases: Cryptocurrencies are used for remittances, smart contracts, and decentralized applications, all of which contribute to their allure.
\n
\n
\n
\n\n
Security Concerns Surrounding CBDCs and Private Cryptocurrencies
\n
In the digital currency race, security remains paramount. The unique security challenges faced by both CBDCs and private cryptocurrencies include:
\n
- \n
- CBDCs: Centralized databases are potential targets for hackers, raising questions about the safety of users’ deposits.
- Private Cryptocurrencies: While cryptography secures transactions, private exchanges often lack adequate compliance measures, increasing the risk of fraud.
\n
\n
\n\n
Case Study: Vietnam’s Digital Currency Aspirations
\n
Vietnam offers a compelling case study as it evaluates the implementation of CBDCs. As highlighted in recent discussions, its central bank is also focusing on enhancing the tiêu chuẩn an ninh blockchain to champion the safe adoption of digital assets. This cautious approach is evident in regulatory proposals aimed at integrating blockchain technology while also protecting consumer interests.
\n\n
Projected User Growth in Vietnam
\n\n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n \n
| Year | Number of Users | Growth Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 3 million | – |
| 2024 | 3.45 million | 15% |
| 2025 | 4 million | 16% |
\n
Source: Vietnam Blockchain Association
\n\n
Conclusion
\n
As we anticipate the digital currency dynamics of 2025, the choice between CBDCs and private cryptocurrencies will hinge on various factors including security, user preference, and regulatory environments. It is a critical moment for stakeholders to understand these dimensions, especially in emerging markets like Vietnam. With the rapid growth and adoption trends of both CBDCs and private cryptocurrencies, the next few years will be pivotal for digital currencies globally.
\n
For more insights and in-depth analysis, visit coinmachinvestment.
Author: Dr. Anna Nguyen, a blockchain security expert, has published over 30 papers in digital asset technology and led audits for various high-profile projects.